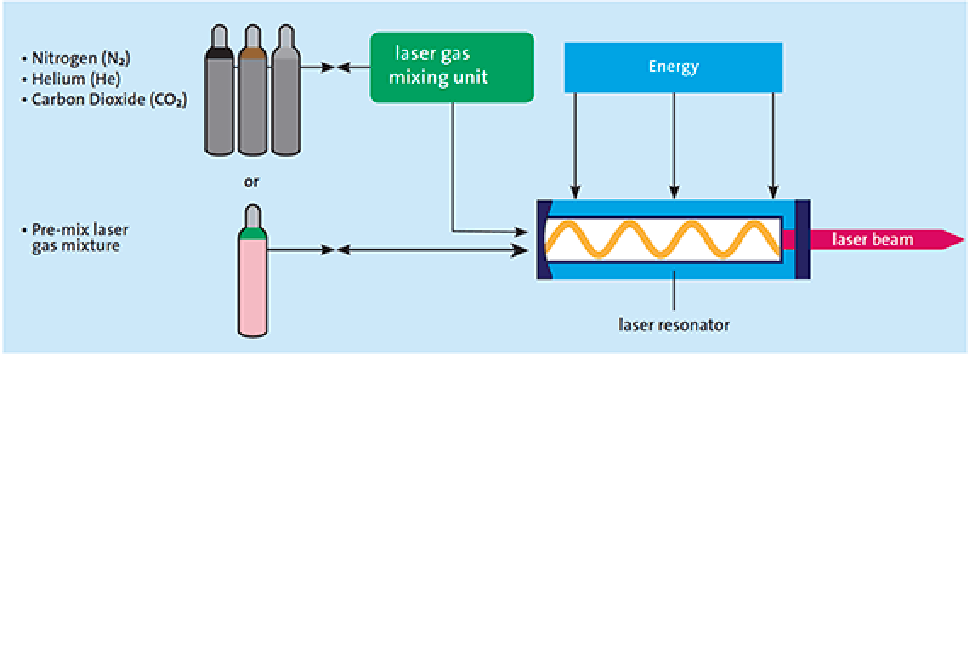
Experis® Resonator Gases
We have a complete range of high quality resonator gases. These pure and pre-mixed gases meet or exceed the gas purity and mix accuracy specifications of the world’s leading laser manufacturers. Experis® resonator gases ensure the highest quality beam characteristics are consistently achieved, allowing you to optimise laser performance and reduce your running costs.
DOWNLOAD EXPERIS® RESONATOR GASES BROCHURE
Protect your investment
CO2 lasers require resonator gases to be very pure. Even the slightest impurity can lead to non-optimal efficiency or even cause damage to the laser. Click below to read our article.
READ MORE